Web hosting has significantly transformed over the years, evolving alongside technological advancements and the ever-growing demands of internet users. The journey of web hosting, from the early days of simple shared hosting to today’s sophisticated cloud hosting solutions, mirrors the broader evolution of the internet itself. You might wonder how it all started, what has changed, and what the future holds. That’s why we’re exploring the Evolution of Web Hosting from Shared to Cloud Hosting.
In this article, we’ll cover the evolution of web hosting, explain what shared, VPS/dedicated, and cloud hosting are, who uses them, and provide a comprehensive comparison to help you understand them more easily. Let’s get started!
Web Hosting and its history

Web hosting is a service that allows individuals and organizations to make their websites accessible via the Internet. When you create a website, the files that make up your site—such as HTML, images, and scripts—need storage so visitors can access them. Web hosting providers offer the technology and infrastructure to store these files on servers.
Not only does web hosting allow you to host websites, but it also supports different types of web apps and CMSs like WordPress across the internet using various technologies. Several types of web hosting are available, including shared hosting, VPS hosting, dedicated hosting, and cloud hosting. Each type offers different levels of performance, control, and scalability to meet various needs.
The concept of web hosting began in the early 1990s. Initially, universities, research institutions, and tech-savvy individuals operated their own servers to provide hosting. These early servers were often maintained privately. As the internet grew, the need for more accessible and reliable servers increased, leading to the development of web hosting services, which we will explore in detail.
What is shared Hosting?
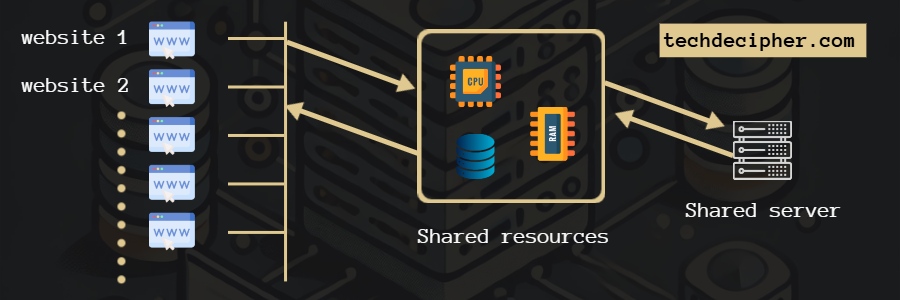
Shared hosting is one of the earliest forms of web hosting. In this model, multiple websites share a single physical server’s resources, such as CPU, RAM, and storage. Each website receives a portion of the server’s resources, making shared hosting a cost-effective solution for individuals and small businesses just starting with their online presence.
Who uses Shared Hosting?
Shared hosting is indeed affordable but comes with some limitations. Since many users share the resources, performance can be inconsistent, especially during peak times. Additionally, shared hosting providers typically don’t allow users to make changes to their shared servers. Individuals and small businesses starting out with their online presence use Shared hosting. If you want to begin without significant investment, for example, by creating a personal blog or small website, shared hosting is a good fit.
Intent: Personal Blogs, personal websites, small business websites.
Top 5 Providers: GoDaddy, NameCheap, HostGator, SiteGround, A2 Hosting, InMotion Hosting.
What is VPS / Dedicated Hosting?

As the web evolved and websites became more complex, the limitations of shared hosting became more apparent. In the early 2000s, as businesses increasingly recognized the importance of a strong online presence, the demand for more robust hosting solutions grew. This led to the development of Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting. VPS hosting divides a physical server into several virtual servers, each with its own dedicated resources.
On the other hand, Dedicated hosting provides a server with all the features and benefits of VPS plus full access to the physical machine. Dedicated Servers, also known as bare metal servers, give you full control over the physical server.
Who uses VPS/Dedicated Hosting?
VPS (Virtual Private Server) hosting and dedicated hosting are typically chosen by users who require more power, control, and customization than shared hosting can offer. Large eCommerce websites, established firms, or companies and developers are a good fit for this type of hosting. However, managing a Dedicated/VPS server requires expertise in server administration, so this option is not ideal for non-tech users.
Intent: Growing Businesses, E-commerce Websites, Developers and Tech-Savvy Users and High-Traffic Websites.
Top 5 Providers: BlueHost, NameCheap, HostGator, SiteGround, A2 Hosting, InMotion Hosting.
What is Cloud Hosting?

The advent of cloud computing in the mid-2000s revolutionized the web hosting industry. Traditional web hosting types had limitations in scalability and flexibility. When existing server resources were exhausted, upgrading to higher tiers was necessary. This often led to downtime until the server upgrade was complete, causing disruptions during business hours. Users sought a robust solution to address these issues, leading to the emergence of cloud hosting.
Cloud hosting is a type of hosting where websites are hosted on a network of interconnected servers (the cloud), rather than on a single physical server. This model offers scalability, reliability, and flexibility that were previously unattainable with traditional hosting solutions.
Who uses cloud hosting?
Cloud hosting is favored by businesses and individuals who need scalable, reliable, and flexible hosting solutions. It’s a good fit for companies that expect or experience fluctuating traffic volumes and need the ability to scale resources up or down quickly. Large online stores that experience variable traffic and require consistent performance during peak shopping periods often opt for cloud hosting.
Intent: Growing Businesses, Large Enterprises, E-commerce Giants, App Developers, Media and Content Providers, and startups.
Top 5 Providers: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft Azure, DigitalOcean, Linode.
Shared hosting vs VPS hosting vs Cloud hosting comparison
| Comparison | Shared Hosting | VPS/Ded Hosting | Cloud Hosting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Most affordable option. | Expensive due to dedicated resources. | Cost-effective with a pay-as-you-go model. |
| Control | Limited control over server settings. | Greater control over server configuration. | High level of control with scaling. |
| Capacity | Limited capacity, best for small sites. | Moderate capacity, handles more traffic. | Superior capacity, scales with demand. |
Conclusion
Whether you’re just starting out with a small website or managing a large-scale application, understanding the different types of hosting and their benefits can help you make informed decisions that best suit your needs. This concludes the evolution of Web Hosting from Shared to Cloud. Which Web Hosting would you prefer and why? Do let us know in the comments section below. If you need any help or have any suggestions to make, then do reach us via the contact page here. Happy Bonaire Flag Day!









